Gastrointestinal diseases significantly impact global health, with some conditions posing serious threats to well-being and even being life-threatening.

In the realm of medical science and diagnostics, few areas are as complex and crucial as the study of gastrointestinal health. Understanding the intricate workings of our digestive system is key to unlocking the mysteries of numerous health conditions that affect millions globally.
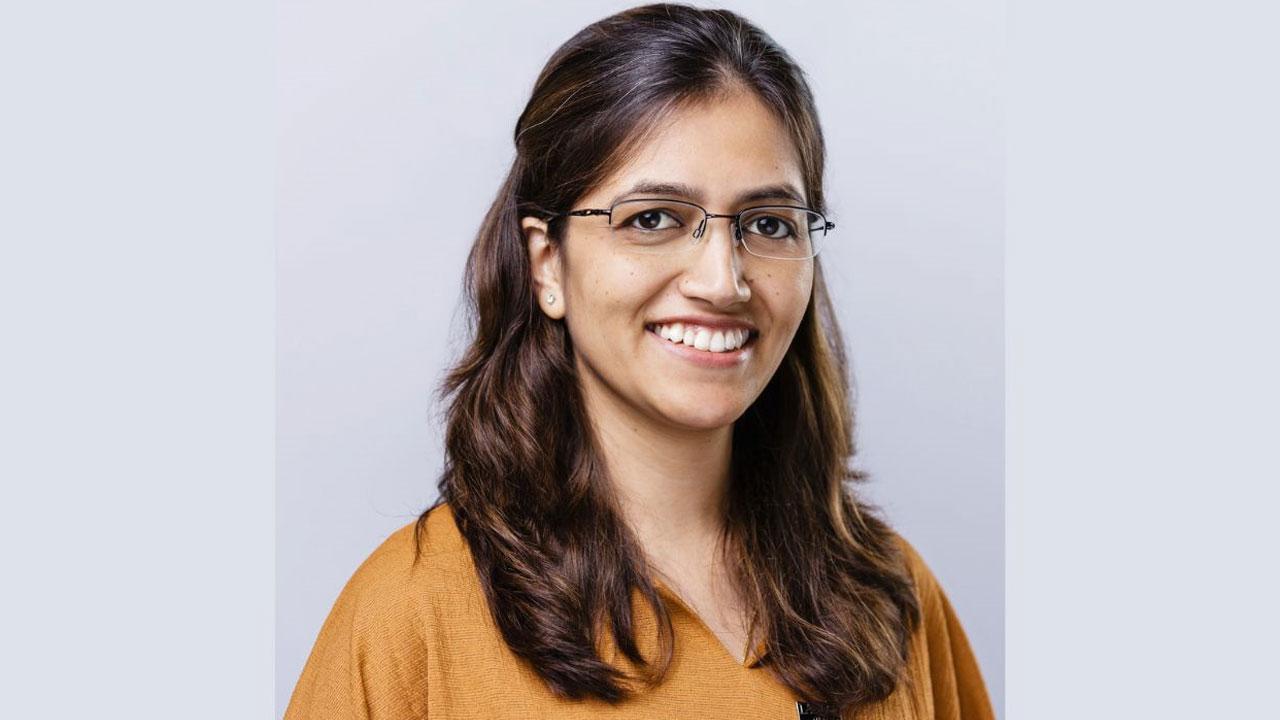
In India, the burden of gastroenterological diseases is significant and varies across different conditions. According to the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study, the number of IBD patients in India was estimated to be 2.7 lakhs (0.27 million) in 2019, which increased from 1.3 lakhs in 1990. To shed light on this vital topic, we had the privilege of conducting an exclusive interview with Dr. Shivani Sharma, the esteemed Vice-President of Pathology Services and Lab Director at CORE Diagnostics.
ADVERTISEMENT
Dr. Sharma, with her extensive expertise and experience in the field of pathology, offers a unique perspective on the challenges and advancements in diagnosing and treating gastrointestinal issues. In this insightful conversation, she delves into the nuances of various gastric-related diseases, their symptoms, and the latest diagnostic techniques. Her role at CORE Diagnostics, a leading facility in medical testing and analysis, places her at the forefront of cutting-edge research and innovation in gastrointestinal health.

Q1: What are gastric related diseases?
Gastric related diseases encompass a broad spectrum of conditions affecting the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, which includes the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine (colon), rectum, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas. These diseases range from benign and transient symptoms to chronic disorders and potentially life-threatening conditions.
Common issues like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcers, and gastritis often stem from inflammation or irritation of the stomach lining. GERD, for instance, occurs when stomach acid frequently flows back into the tube connecting your mouth and stomach (esophagus). This backwash (acid reflux) can irritate the lining of your esophagus, leading to discomfort and long-term complications if untreated.
Treatment for gastric-related diseases varies depending on the specific condition but may include medications to reduce acid production, antibiotics to clear up infections, lifestyle changes, and in severe cases, surgery. For chronic conditions like IBD and gastrointestinal cancers, treatment often involves a combination of medication, dietary changes, and sometimes surgical intervention to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Understanding the wide range of gastric-related diseases is crucial for early detection and effective management. Regular medical check-ups, awareness of symptoms, and a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk and impact of these conditions.
Q2: What are some main gastrointestinal diseases that can be life-threatening?
Gastrointestinal diseases significantly impact global health, with some conditions posing serious threats to well-being and even being life-threatening. The main gastrointestinal diseases include a variety of disorders, each affecting different parts of the digestive system.
Constipation and Diarrhea: Common yet often overlooked, these conditions can be symptoms of underlying digestive disorders. Chronic constipation may lead to complications like hemorrhoids or fecal impaction, while persistent diarrhea can result in severe dehydration and nutrient deficiencies.
Acid Reflux and GERD: Acid reflux is a common condition where stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing heartburn and discomfort. When this becomes chronic, it is known as Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD), which can lead to more serious complications like esophageal ulcers or Barrett's esophagus, a precursor to esophageal cancer.
Gallstones: These are hard deposits that form in the gallbladder, often causing severe pain and leading to complications like cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder) or pancreatitis.
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD): This group includes Crohn's disease and Ulcerative Colitis, chronic conditions that cause long-term inflammation of the GI tract. They can lead to severe complications like bowel obstruction, ulcers, and increased risk of colorectal cancer.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): A common disorder affecting the large intestine, IBS is characterized by symptoms like cramping, abdominal pain, bloating, gas, and diarrhea or constipation. While not life-threatening, it significantly impacts the quality of life.
Hemorrhoids: Swollen veins in the lower rectum and anus, often a result of chronic constipation, can cause discomfort and bleeding.
Gastrointestinal and Colorectal Cancers: These are among the most serious GI conditions. They often develop from polyps in the colon or rectum and can be life-threatening if not detected early. Symptoms may include changes in bowel habits, blood in stool, unexplained weight loss, and fatigue.
Early detection and treatment of these diseases are crucial. Lifestyle changes, medications, and in some cases, surgery, are key to managing these conditions. Regular screenings, especially for high-risk individuals, are vital for early cancer detection. Awareness and education about these diseases can lead to earlier diagnosis and better outcomes.
Q3: What symptoms should people be aware of, and how can these issues be detected and treated early?
Gastric problems can manifest in various forms, and recognizing their symptoms is crucial for early detection and treatment. Common symptoms include:
Abdominal Pain and Discomfort: One of the most frequent indicators of gastric issues, ranging from mild discomfort to severe pain.
Bloating and Gas: Feelings of fullness or swelling in the abdomen, often accompanied by excessive gas.
Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms can indicate a range of issues, from mild infections to serious conditions like ulcers or cancer.
Heartburn: A burning sensation in the chest, often after eating, caused by acid reflux.
Changes in Bowel Habits: Including constipation or diarrhea, which can be symptoms of conditions like IBS or IBD.
Loss of Appetite and Weight Loss: Unintended weight loss or a decrease in appetite can be signs of more serious conditions, including cancer.
Early detection of gastric problems is key to effective treatment and can prevent the progression to more serious conditions. Routine medical check-ups and being attentive to bodily changes are essential. If symptoms persist or worsen, it's important to consult a healthcare professional.
Diagnostic tests play a crucial role in detecting gastric issues. These may include:
Endoscopy: To examine the upper digestive system using a tiny camera on a long, flexible tube.
Colonoscopy: For inspecting the colon and rectum, often used to screen for colorectal cancer.
Imaging Tests: Such as CT scans, MRI, and ultrasounds to visualize the digestive tract.
Blood Tests: To check for infections, anemia, or other conditions that can be associated with gastric problems.
Stool Tests: Useful for detecting infections, bleeding, or problems like malabsorption.
Treatment varies based on the specific condition but often includes dietary changes, medications to manage symptoms or treat infections, and in some cases, surgery. For instance, acid blockers or proton pump inhibitors are used for GERD, while antibiotics may be necessary for bacterial infections like H. pylori.
Preventive measures like a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding triggers like spicy foods, alcohol, and smoking can also help in managing and preventing gastric issues. Stress management is another important aspect, as stress can exacerbate many gastric conditions.
Understanding these symptoms and the importance of early detection can empower individuals to seek timely medical attention, leading to better health outcomes.
Q4: Are Gastrointestinal Issues more prevalent worldwide or just in India?
Gastrointestinal issues are a global health concern, affecting millions of people across different regions and cultures. The prevalence and increase of these conditions can be attributed to various factors, including dietary habits, lifestyle changes, and increased awareness and diagnosis.
Global Prevalence: Gastrointestinal disorders, ranging from common conditions like GERD and IBS to more severe diseases like colorectal cancer, are widespread. The World Gastroenterology Organisation notes that digestive diseases are a significant cause of mortality and morbidity worldwide.
Regional Variations: The prevalence of certain gastrointestinal disorders varies by region. For instance, IBS is more common in Western countries, while gastrointestinal infections are more prevalent in developing countries due to factors like water quality and sanitation.
Rising Incidence in Developing Countries: Rapid urbanization and lifestyle changes in developing countries, including dietary changes and increased stress, have led to a rise in gastrointestinal issues traditionally more common in developed nations.
Diet and Lifestyle Factors: The global increase in processed foods, high in fat and sugar, coupled with sedentary lifestyles, contributes to the rise in gastrointestinal problems. Obesity, a growing global epidemic, is a significant risk factor for many digestive diseases, including GERD and colorectal cancer.
Aging Population: With the global increase in life expectancy, there is a higher prevalence of gastrointestinal issues that tend to affect older adults, such as colorectal cancer and diverticular disease.
Increased Awareness and Diagnosis: Improved healthcare access and advancements in medical technology have led to increased diagnosis and reporting of gastrointestinal conditions. People are more aware of the symptoms and are seeking medical advice earlier.
Data and Statistics: According to the Global Burden of Disease study, digestive diseases accounted for substantial health loss globally, with a notable increase over the past decades. In India, a study reported that about 18% of the population suffers from some form of stomach disorder, with a slightly higher prevalence in men.
The increasing trend of gastrointestinal issues worldwide calls for a global health response, focusing on preventive measures, early diagnosis, and effective management strategies. Public health initiatives aimed at promoting healthy diets, regular physical activity, and awareness about the importance of gastrointestinal health are crucial in addressing this growing concern.
Q5: How can a gastroenterologist assist patients?
Gastroenterologists play a pivotal role in diagnosing, treating, and managing a wide range of gastrointestinal (GI) disorders. Their expertise is crucial in ensuring patient well-being, especially for those suffering from chronic or complex GI conditions.
Diagnosis: Gastroenterologists are trained to diagnose GI diseases accurately. They use a variety of diagnostic tools, including endoscopy, colonoscopy, and imaging techniques like CT scans and MRIs. These procedures help them visualize the GI tract and identify issues ranging from inflammation and ulcers to tumors.
Treatment: Once a diagnosis is made, gastroenterologists develop a treatment plan tailored to the patient's specific condition. This may include medication, dietary recommendations, and in some cases, endoscopic procedures or surgery. For chronic conditions like IBD or IBS, treatment often involves long-term management strategies to control symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
Preventive Care: Gastroenterologists also play a key role in preventive care, particularly in the context of colorectal cancer. They perform screening colonoscopies, which can detect precancerous polyps early, significantly reducing the risk of developing colorectal cancer.
Patient Education: Educating patients about their conditions is a vital part of a gastroenterologist's role. This includes advising on dietary modifications, lifestyle changes, and understanding the effects and management of their condition.
Research and Advancements: Many gastroenterologists are involved in research, contributing to advancements in the understanding and treatment of GI diseases. This research can lead to the development of new treatments and therapies, improving patient outcomes.
Collaborative Care: Gastroenterologists often work in collaboration with other specialists, such as dietitians, oncologists, and surgeons, to provide comprehensive care to patients, especially those with complex or advanced GI diseases.
The role of gastroenterologists is integral to the healthcare system, particularly given the prevalence and impact of GI diseases globally. Their expertise not only helps in managing acute and chronic conditions but also plays a significant role in preventive health, ultimately enhancing the quality of life for patients with GI disorders.
Q6: What preventive measures should patients take?
Prevention plays a crucial role in maintaining gastrointestinal health and preventing the onset or exacerbation of GI disorders. Adopting certain lifestyle and dietary habits like balanced diet, hydration, limiting processed foods, moderating alcohol and caffeine, avoiding smoking, regular exercise, and regular health check-ups can significantly reduce the risk of developing various gastrointestinal issues.
By incorporating these preventive measures into daily life, individuals can significantly improve their gastrointestinal health and reduce the risk of developing GI disorders. It's important to remember that a proactive approach to health, including regular consultations with healthcare providers, is key to maintaining long-term digestive wellness.
Q7: What type of tests does CORE Diagnostics offer?
CORE Diagnostics offers a comprehensive range of tests specifically tailored for diagnosing and managing gastrointestinal (GI) issues. Their portfolio includes a variety of advanced diagnostic procedures and tests, which are crucial in accurately identifying a wide array of gastric, intestinal, and infectious diseases. Here are some of the key types of tests provided by CORE Diagnostics: Hepatitis Virus Testing, Fecal Calprotectin, Fecal Elastase, Celiac Comprehensive Profile, H. pylori, Gilbert Syndrome, UGT1A1 Genotyping, Anti-LKM, Auto-immune Hepatitis Panel, Biofire Gastrointestinal Panel, Food Intolerance Panel, TTG DGP Screen, c-KIT, specialized gastric biopsy markers like: Her-2 neu, MMR, CEA, CA19.9, CD117, DOG1, MUC2, CDX2, CK7, CK20, SATB2, SDHB, CA125, HepPar1, CALRETININ, MUC5AC, BETA-CATENIN, H-CALDESMON, PanCK, immuno-suppressant drug level tests such as: Sirolimus, Everolimus, Tacrolimus, etc. and infectious disease tests such as HIV, Cytomegalovirus, BK Virus, etc.
CORE Diagnostics' extensive range of tests plays a vital role in the comprehensive assessment and management of gastrointestinal health, offering advanced diagnostic capabilities for a wide array of conditions.
 Subscribe today by clicking the link and stay updated with the latest news!" Click here!
Subscribe today by clicking the link and stay updated with the latest news!" Click here!